Overview
Erosive tooth wear is a common but often overlooked dental condition that can significantly impact your oral health. Unlike cavities caused by bacteria, this type of tooth damage occurs when acids gradually wear away the enamel. Whether from dietary habits, acid reflux, or other factors, erosive tooth wear can affect anyone. This page is designed to help you understand the causes, warning signs, and effective prevention strategies to help protect your teeth from unnecessary erosion.
Quick Links
About Erosive Tooth Wear
What is Erosive Tooth Wear?
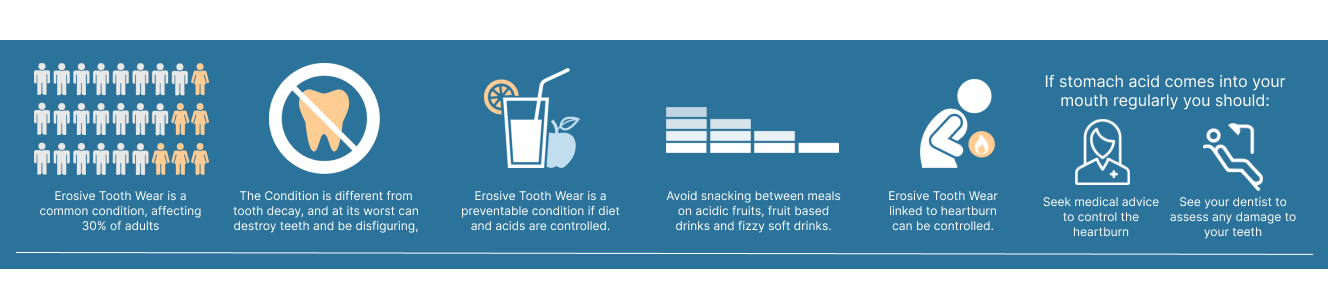
When you look at your teeth, they seem solid, but actually the enamel, the outer layer of your tooth, can slowly dissolve if it’s surrounded by acid, such as that found in fruit juices or some fizzy drinks; this is known as ‘erosion’.
- Erosion starts when minerals are removed from your teeth and softens the enamel
- The ingredients for re-hardening your teeth are found in saliva and fluoride in toothpastes so the softening can be repaired.
Erosive Tooth Wear most often occurs on your front teeth and the biting surfaces of your back teeth
- Part or all of the outer layer of tooth, the enamel, may eventually be lost, exposing the inner layer, (the dentin). This inner layer is more yellow and once exposed changes the colour of the teeth.
- You are not alone, erosive tooth wear is common, about a third of all adults have it, though few have it severely
- Read more about the structure of your teeth and how acid affects your teeth.
Causes of erosive tooth wear
One of the most common ways to wear away the tooth is by drinking and eating acidic drinks and foods outside meal times.
A number of drinks and some foods can contribute to erosive tooth wear but the amount of times you consume these, especially by frequent snacking, can also influence the amount of erosion.

Fruit

Fruit-based drinks containing citric acid

Carbonated drinks

Alcoholic drinks

Acidic sweets

Other foods
Other causes can include:
Signs & Symptoms
Changes may occur in the colour, shape and/or appearance of your teeth.
Teeth may:

Become yellow in appearance

Change in shape

Become glassy in appearance

Become shorter

Cause pain when teeth come into contact with hot/cold
It may be your dentist who first notices this but don’t wait, make an appointment if you are concerned about this, even if your teeth aren’t hurting.
Prevention & Treatment
Video Library
You can read more in our Patient FAQ's or in the following articles:

